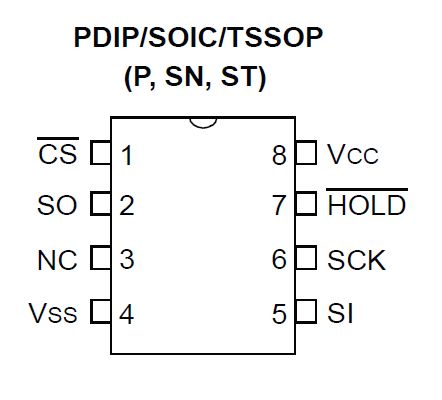
SI(5)はCPUのMOSIに接続します
SO(2)はCPUのMISOに接続します
SCK(6)はCPUのSCKに接続します
/HOLD(7)は特別なことをしないのでhighに接続します
/CS(1)は選択するためにCPUに接続します。
 |
32kBのSRAMです。 SI(5)はCPUのMOSIに接続します SO(2)はCPUのMISOに接続します SCK(6)はCPUのSCKに接続します /HOLD(7)は特別なことをしないのでhighに接続します /CS(1)は選択するためにCPUに接続します。 |
| Ser23K256.h |
|---|
/** Ser23K256 - drive the Microchip 23K256 SRAM using SPI
* Copyright (c) 2010 Romilly Cocking
* Released under the MIT License: http://mbed.org/license/mit
*
* 23K256 data sheet at http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/22100B.pdf
*
* Page-mode commands have not been implemented; I have found no need for them yet.
*
* Assumes spi mode is default (8,0).
*
* You can clock the 23K256 at up to 20MHz, so it supports the mbed's maximum SPI frequency of 12MHz.
*/
#include "mbed.h"
#ifndef SER23K256_H
#define SER23K256_H
// mode codes for 23K256
#define BYTE_MODE 0x00
#define SEQUENTIAL_MODE 0x40
// command codes for 23K256
#define READ 0x03
#define WRITE 0x02
#define READ_STATUS 0x05 // called RDSR in datasheet
#define WRITE_STATUS 0x01 // called WRSR in datasheet
/** An interface for the Microchip 32k byte 23K256 SRAM over SPI
*
*
*
* @code
* #include "mbed.h"
* #include "Ser23K256.h"
*
*
* SPI spi(p5,p6,p7);
* Ser23K256 sram(spi,p14);
*
* int main() {
* char buff[50];
* sram.write(0, 'h');
* sram.write(1, 'i');
* sram.write(2, '!');
* sram.write(3, '\0');
* for (int address = 0; address < 4; address++) {
* buff[address] = sram.read(address);
* }
* printf("sram = %s\r\n", buff);
* sram.write(0, "Hello world!",12);
* sram.read(0, buff, 12);
* buff[12]='\0';
* printf("now = %s\r\n", buff);
*}
* @endcode
* connections:
* chip pin 1 to mbed ncs (see below)
* chip pin 2 SO to mbed MISO
* chip pin 3 - no connection
* chip pin 4 to mbed Gnd
* chip pin 5 SI pin to mbed MOSI
* chip pin 6 SCK to mbed sck
* chip pin 7 (notHOLD) to mbed Vout
* chip pin 8 to mbed Vout
*/
class Ser23K256 {
public:
/** Create an interface
*
*
* @param spi An SPI object
* @param ncs Not chip select pin - any free Digital pin will do
*/
Ser23K256(SPI& spi, PinName ncs);
/** read a byte from SRAM
* @param address The address to read from
* @return the character at that address
*/
char read(int address);
/** read multiple bytes from SRAM into a buffer
* @param address The SRAM address to read from
* @param buffer The buffer to read into (must be big enough!)
* @param count The number of bytes to read
*/
void read(int address, char * buffer, int count);
/** write a byte to SRAM
* @param address The address SRAM to write to
* @param byte The byte to write there
*/
void write(int address, char byte);
/** write multiple bytes to SRAM from a buffer
* @param address The SRAM address write to
* @param buffer The buffer to write from
* @param count The number of bytes to write
*/
void write(int address, char * buffer, int count);
private:
SPI& _spi;
DigitalOut _ncs;
char readStatus();
void writeStatus(char status);
void prepareCommand(char command, int address);
void select();
void deselect();
};
#endif
|
| Ser23K256.cpp |
|---|
/* Ser23K256 - drive the Microchip 23K256 SRAM using SPI
* Copyright (c) 2010 Romilly Cocking
* Released under the MIT License: http://mbed.org/license/mit
*/
#include "mbed.h"
#include "Ser23K256.h"
Ser23K256::Ser23K256(SPI& spi, PinName ncs) : _spi(spi), _ncs(ncs) {
deselect();
}
void Ser23K256::select() {
_ncs = 0;
}
void Ser23K256::deselect() {
_ncs = 1;
}
void Ser23K256::writeStatus(char status) {
select();
_spi.write(WRITE_STATUS);
_spi.write(status);
deselect();
}
char Ser23K256::readStatus() {
select();
_spi.write(READ_STATUS);
char result = (char) _spi.write(0);
deselect();
return result;
}
void Ser23K256::prepareCommand(char command, int address) {
select();
_spi.write(command);
_spi.write(address >> 8);
_spi.write(address & 0xFF);
}
// write or read a single byte
void Ser23K256::write(int address, char byte) {
prepareCommand(WRITE, address);
_spi.write(byte);
deselect();
}
char Ser23K256::read(int address) {
prepareCommand(READ, address);
int result = _spi.write(0);
deselect();
return (char) result;
}
// buffered write and read
/*
* the single-byte read and write assume the 23K256 is in its default byte-mode
* so sequential-model commands must switch the chip into sequential mode
* at the start and return it to byte mode at the end.
*/
void Ser23K256::write(int address, char * buffer, int count) {
writeStatus(SEQUENTIAL_MODE);
prepareCommand(WRITE, address);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
_spi.write(buffer[i]);
}
deselect();
writeStatus(BYTE_MODE);
}
void Ser23K256::read(int address, char * buffer, int count) {
writeStatus(SEQUENTIAL_MODE);
prepareCommand(READ, address);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
buffer[i] = _spi.write(0);
}
deselect();
writeStatus(BYTE_MODE);
}
|
| main.cpp |
|---|
#include "mbed.h"
#include "Ser23K256.h"
SPI spi(p5,p6,p7);
Ser23K256 sram(spi,p14);
Serial pc(USBTX, USBRX); // tx, rx
int main() {
pc.baud(115200);
char buff[50];
sram.write(0, 'h');
sram.write(1, 'i');
sram.write(2, '!');
sram.write(3, '\0');
for (int address = 0; address < 4; address++) {
buff[address] = sram.read(address);
}
pc.printf("sram = %s\r\n", buff);
sram.write(0, "Hello world!",12);
sram.read(0, buff, 12);
buff[12]='\0';
pc.printf("now = %s\r\n", buff);
}
|
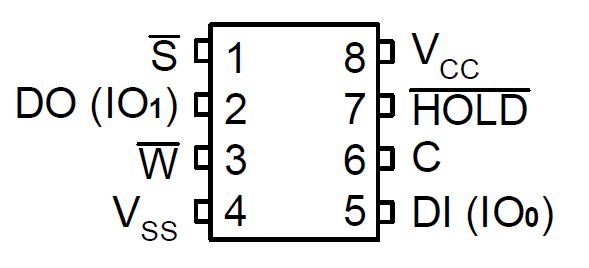 |
4MBのflashメモリです。 DI(5)はCPUのMOSIに接続します DO(2)はCPUのMISOに接続します C(6)はCPUのSCKに接続します /HOLD(7)は特別なことをしないのでhighに接続します /S(1)は選択するためにCPUに接続します。 /W(3)は読み書き信号のためにCPUに接続します。 |
| A25L032.h |
|---|
// A25L032.h
#ifndef A25L032_H
#define A25L032_H
#include "mbed.h"
#define SPI_FREQ 40000000 // 40MHz
//#define SPI_FREQ 1000000 // 1MHz
#define SPI_MODE 0
#define SPI_NBIT 8
#define WE_INST 0x06
#define READ_STATUS 0x05 // called RDSR-1 in datasheet
#define READ_STATUS2 0x35 // called RDSR-2 in datasheet
#define WD_INST 0x04
#define R_INST 0x03
#define W_INST 0x02
#define WRITE_STATUS 0x01 // called WRSR in datasheet
#define C_ERASE_INST 0x60 // chip erase
#define DUMMY_ADDR 0x00
#define ADDR_BMASK2 0x00ff0000
#define ADDR_BMASK1 0x0000ff00
#define ADDR_BMASK0 0x000000ff
#define ADDR_BSHIFT2 16
#define ADDR_BSHIFT1 8
#define ADDR_BSHIFT0 0
class A25L032: public SPI {
public:
A25L032(PinName mosi, PinName miso, PinName sclk, PinName cs);
int readByte(int addr); // takes a 24-bit (3 bytes) address and returns the data (1 byte) at that location
int readByte(int a2, int a1, int a0); // takes the address in 3 separate bytes A[23,16], A[15,8], A[7,0]
void readStream(int addr, char* buf, int count); // takes a 24-bit address, reads count bytes, and stores results in buf
void writeByte(int addr, int data); // takes a 24-bit (3 bytes) address and a byte of data to write at that location
void writeByte(int a2, int a1, int a0, int data); // takes the address in 3 separate bytes A[23,16], A[15,8], A[7,0]
void writeStream(int addr, char* buf, int count); // write count bytes of data from buf to memory, starting at addr
void chipErase(); // erase all data on chip
int readStatus();
int readStatus(int n);
void writeStatus(int status);
private:
void writeEnable(); // write enable
void writeDisable(); // write disable
void chipEnable(); // chip enable
void chipDisable(); // chip disable
DigitalOut _cs;
};
#endif
|
| A25L032.cpp |
|---|
// A25L032.cpp
#include"A25L032.h"
extern Serial pc;
// CONSTRUCTOR
A25L032::A25L032(PinName mosi, PinName miso, PinName sclk, PinName cs) : SPI(mosi, miso, sclk), _cs(cs) {
this->format(SPI_NBIT, SPI_MODE);
this->frequency(SPI_FREQ);
chipDisable();
}
// READING
int A25L032::readByte(int addr) {
chipEnable();
this->write(R_INST);
this->write((addr & ADDR_BMASK2) >> ADDR_BSHIFT2);
this->write((addr & ADDR_BMASK1) >> ADDR_BSHIFT1);
this->write((addr & ADDR_BMASK0) >> ADDR_BSHIFT0);
int response = this->write(DUMMY_ADDR);
chipDisable();
return response;
}
int A25L032::readByte(int a2, int a1, int a0) {
chipEnable();
this->write(R_INST);
this->write(a2);
this->write(a1);
this->write(a0);
int response = this->write(DUMMY_ADDR);
chipDisable();
return response;
}
void A25L032::readStream(int addr, char* buf, int count) {
if (count < 1)
return;
chipEnable();
this->write(R_INST);
this->write((addr & ADDR_BMASK2) >> ADDR_BSHIFT2);
this->write((addr & ADDR_BMASK1) >> ADDR_BSHIFT1);
this->write((addr & ADDR_BMASK0) >> ADDR_BSHIFT0);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
buf[i] = this->write(DUMMY_ADDR);
chipDisable();
}
// WRITING
void A25L032::writeByte(int addr, int data) {
writeByte((addr & ADDR_BMASK2) >> ADDR_BSHIFT2,
(addr & ADDR_BMASK1) >> ADDR_BSHIFT1,
(addr & ADDR_BMASK0) >> ADDR_BSHIFT0,
data);
}
void A25L032::writeByte(int a2, int a1, int a0, int data) {
writeEnable();
wait_us(0);
chipEnable();
this->write(W_INST);
this->write(a2);
this->write(a1);
this->write(a0);
this->write(data);
chipDisable();
while(readStatus(1)&1);
writeDisable();
}
void A25L032::writeStream(int addr, char* buf, int count) {
if (count < 1)
return;
writeEnable();
wait_us(0);
chipEnable();
this->write(W_INST);
this->write((addr & ADDR_BMASK2) >> ADDR_BSHIFT2);
this->write((addr & ADDR_BMASK1) >> ADDR_BSHIFT1);
this->write((addr & ADDR_BMASK0) >> ADDR_BSHIFT0);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
this->write(buf[i]);
while(readStatus(1)&1);
chipDisable();
writeDisable();
}
//ERASING
void A25L032::chipErase() {
writeEnable();
chipEnable();
this->write(C_ERASE_INST);
while(readStatus(1)&1);
chipDisable();
writeDisable();
}
//ENABLE/DISABLE (private functions)
void A25L032::writeEnable() {
chipEnable();
this->write(WE_INST);
chipDisable();
}
void A25L032::writeDisable() {
chipEnable();
this->write(WD_INST);
chipDisable();
}
void A25L032::chipEnable() {
_cs = 0;
}
void A25L032::chipDisable() {
_cs = 1;
}
int A25L032::readStatus(int n) {
chipEnable();
this->write((n==2) ? READ_STATUS2 : READ_STATUS);
int result = this->write(0);
int result2 = this->write(0);
chipDisable();
return result | result2<<8;
}
int A25L032::readStatus() {
chipEnable();
this->write(READ_STATUS);
int result = this->write(0);
int result3 = this->write(0);
chipDisable();
chipEnable();
this->write(READ_STATUS2);
int result2 = this->write(0);
result3 = this->write(0);
chipDisable();
return result | result2<<8;
}
void A25L032::writeStatus(int status) {
chipEnable();
this->write(WRITE_STATUS);
this->write(status&0xff);
this->write(status>>8);
chipDisable();
}
|
| main.cpp |
|---|
#include "mbed.h"
#include"A25L032.h"
DigitalOut myled(LED1);
Serial pc(USBTX, USBRX); // tx, rx
int main()
{
pc.baud(115200);
char buff[50];
A25L032 flash(p5, p6, p7, p8);
pc.printf("SPI init done\n");
// read previously written data at arbitrary address 0x168
char str[12];
flash.readStream(0x168, str, 12);
pc.printf("%s\n",str);
for(int i=0; i<11; i++) pc.printf("%02x ", str[i]);
pc.printf("\n");
flash.chipErase();
pc.printf("Erase done %04x\n", flash.readStatus(1));
pc.printf("[%02x]\n", flash.readByte(0x00,0x00,0x06));
pc.printf("<%02x>\n", flash.readByte(0x06));
flash.writeByte(0x0, 0x0, 0x06,'a');
flash.writeByte(0x11,'b');
pc.printf("a[%02x]\n", flash.readByte(0x06));
pc.printf("a<%02x>\n", flash.readByte(0x00,0x00,0x06));
pc.printf("b[%02x]\n", flash.readByte(0x11));
pc.printf("b<%02x>\n", flash.readByte(0x00,0x00,0x11));
char string[] = "Japan World";
pc.printf("writeStream\n");
flash.writeStream(0x168, string, 12);
char str2[11] = {0};
flash.readStream(0x168, str2, 12);
pc.printf("%s\n",str2);
for(int i=0; i<12; i++) pc.printf("%02x ", str2[i]);
pc.printf("\n---------------------------------------------\n");
}
|