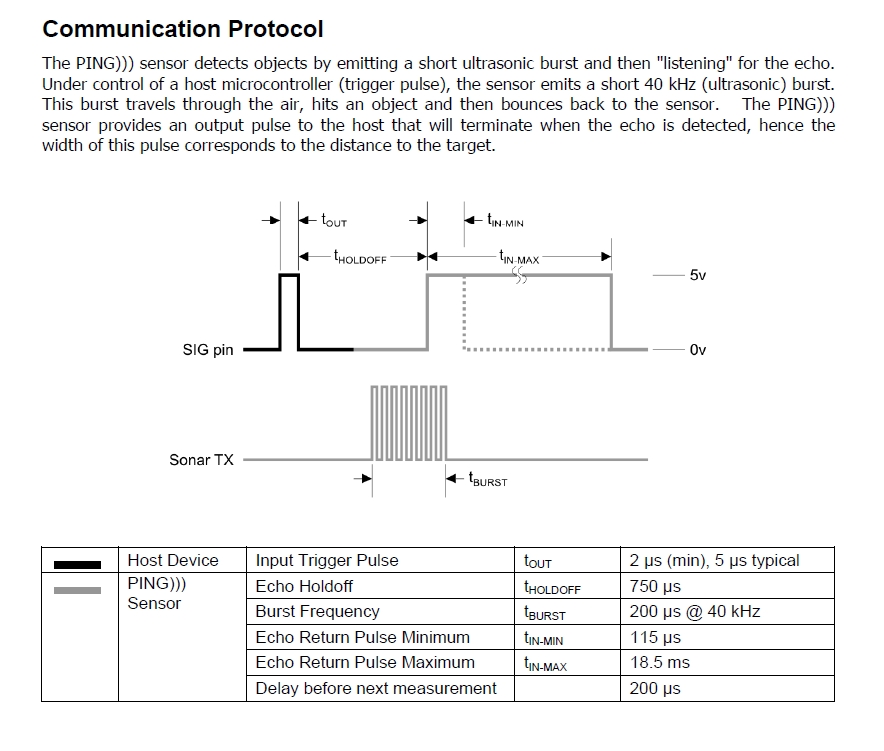
- 用いるIOビットを出力に設定する。
- 1を出力する。
- 約5μ秒1を維持する。
- 0を出力する。
- そのビットを入力に変更する。
- 1になるまで待つ。待つが、最大約18.5msまでしか待たない。
- 0になるまでカウントをする。0になるまで待つが、最大約18.5msまでしか待たない。
- カウントした数が距離に比例する。
- 6,7でタイムアウトの時は1に戻るか、エラーを知らせる。
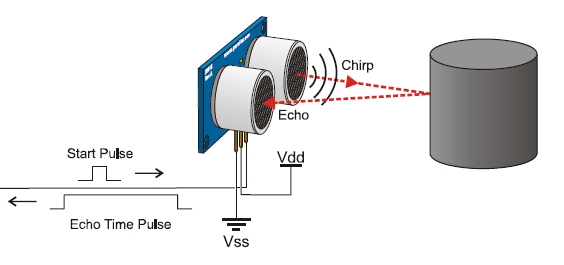
| 通信プロトコル(計測の方法) |
|---|

|


| ping.c |
|---|
/************************************************/
/* PORT7 bit0に超音波レンジファインダーを繋げる */
/************************************************/
int ping(void)
{
int i,count;
IO.PCR7 = 1; // 出力に設定
IO.PDR7.BIT.B0=1;
for(i=0; i<11; i++) ; // 5.28μs パルス
IO.PDR7.BIT.B0=0;
IO.PCR7 = 0; // 入力に設定
count = 0;
while(!IO.PDR7.BIT.B0 && (count++<15000)); // パルス開始を待つ
if(count <= 15000) { // 18.24msで断念
count = 0;
while(IO.PDR7.BIT.B0 && (count++<15000)); // パルス終了を待つ
}
IO.PCR7 = 1; // 出力に設定
IO.PDR7.BIT.B0=0;
return count;
}
|

| 通信プロトコル(計測の方法) |
|---|
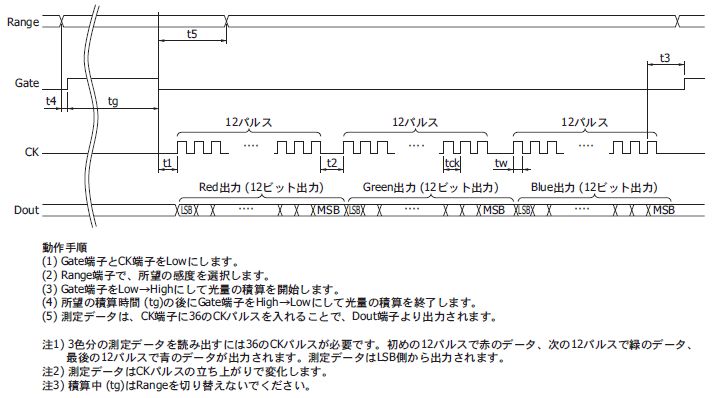 |
| color_sensor.c |
|---|
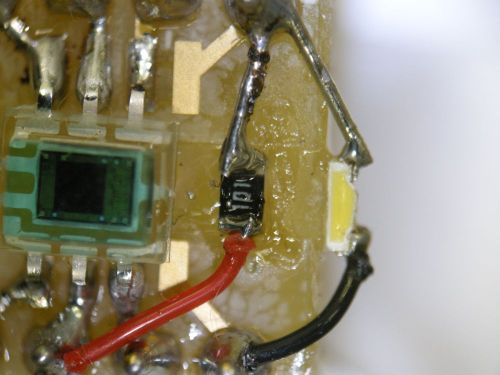
// 関数の値として明るさを返す。配列でRGBの割合を%で返す。
unsigned getRGB(unsigned int RGB[])
{
unsigned int i, j, coldata, intensity=0;
IO.PDR2.BIT.B4=1; // Gate=1
Wait(10); // 10ms 積算時間(不正確)
IO.PDR2.BIT.B4=0; // Gate=0
for(i=0; i<3; i++) {
coldata=0;
for(j=0; j<12; j++) {
IO.PDR2.BIT.B0=1; // CK=1 パルス幅このままで1.5μs
coldata>>=1;
if(IO.PDR7.BIT.B5) coldata|=0x800;
IO.PDR2.BIT.B0=0; // CK=0
}
RGB[i]=coldata;
intensity += coldata;
}
for(i=0; i<3; i++) RGB[i] = RGB[i]*100/intensity;
return intensity;
}
|
unsigned int rgb[3], light; light = getRGB(rgb);プログラム中Wait関数は不正確なので後で出てくるデジタルコンパスのプログラム中にあるdelay関数を利用した方が良いかもしれません。
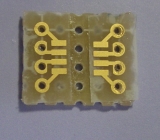
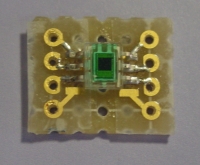
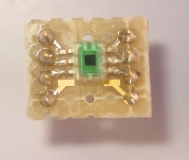
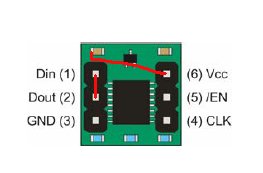
1: Vdd (2.7~5.5Vを供給する) 2: PSD(パワーシャットダウン。Vddに接続で通常動作。GNDか無接続でシャットダウン) 3: GND(グラウンドへ接続) 4: Parity(内部EEPROMのパリティチェック用。通常は無接続) 5: SelfTest(通常はGNDに接続。Vddにつなぐと出力が1G増える) 6: OutX(X軸のアナログ出力) 7: OutY(Y軸のアナログ出力) 8: OutZ(Z軸のアナログ出力)電源は入出力の電圧の違いが出ないようにCPUと同じ3.3Vを使用します。
CN10 チャンネル 1: PB7 7 2: PB6 6 3: PB5 5 4: PB4 4なお、初期のvs-wrc003.cのAdRead関数にはバグか故意かは分かりませんが、PB7とPB6に接続しても計測できません。
 |
 |
| 通信プロトコル |
|---|
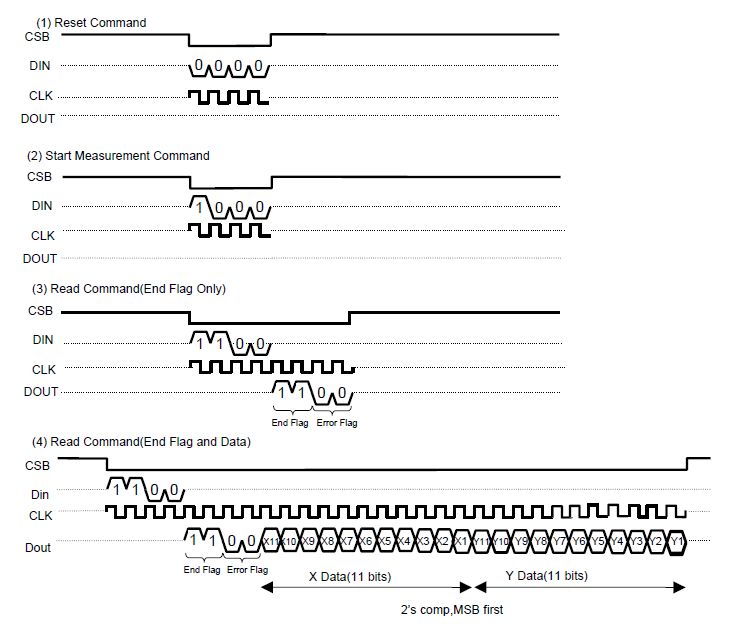 |
| コマンド |
|---|
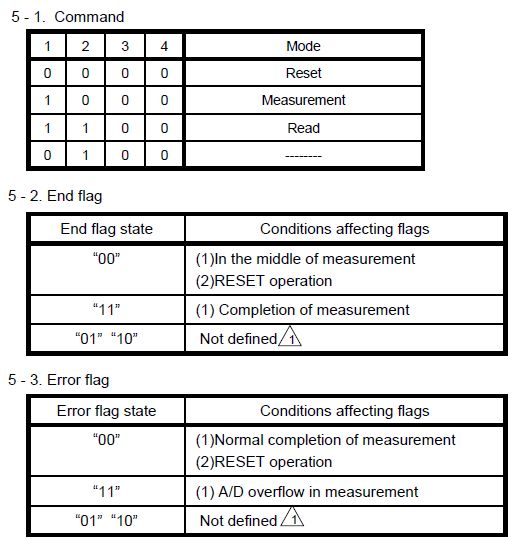 |
| compass.c |
|---|
#include "vs-wrc003.h"
#include "common.h"
void startInit(char* str);
void main(void)
{
startInit("************ デジタルコンパスのテスト ****************\n");
SetCompassHM55B(port8, 5, 6, 7);
CompassStart(); // Start a measurement
while(true) {
if( CompassPoll()) {
printf("%3d\n", getCompassAngle());
Wait(100);
CompassStart(); // Start a measurement
}
}
}
void startInit(char* str)
{
const BYTE MainCycle = 100;
Init((BYTE)MainCycle); //CPUの初期設定
InitSci3(CBR_115200,non,1);
Mtr_Run(0, 0, 0, 0);
while(!getSW() && !inkey());
printf(str);
}
|
| common.h |
|---|
#ifndef _COMMON #define _COMMON #define null -1 #define false 0 #define true 1 #define port1 0xFFD4 #define port2 0xFFD5 #define port3 0xFFD6 #define port5 0xFFD8 #define port6 0xFFD9 #define port7 0xFFDA #define port8 0xFFDB #define portB 0xFFDD #ifndef _VSWRC003_H typedef unsigned char UBYTE; typedef unsigned char BYTE; typedef signed short SWORD; typedef unsigned short UWORD; typedef signed int SINT; typedef unsigned int UINT; typedef signed long SDWORD; typedef unsigned long UDWORD; typedef unsigned char bool; #endif #endif |
| ビットフィールド |
|---|
struct ioBit{ // Bit Access
unsigned char B7:1; // Bit 7
unsigned char B6:1; // Bit 6
unsigned char B5:1; // Bit 5
unsigned char B4:1; // Bit 4
unsigned char B3:1; // Bit 3
unsigned char B2:1; // Bit 2
unsigned char B1:1; // Bit 1
unsigned char B0:1; // Bit 0
} ;
一般的には次のような形のものを言います。shortは16bitの変数で、その16bitの一つの変数の中に、それぞれ1,4,5,6bitの領域に名前をつけてアクセスできるようにする方法です。
struct tag {
short a:1; // 1 ビットのフィールド
short b:4; // 4 ビットのフィールド
short c:5; // 5 ビットのフィールド
short d:6; // 6 ビットのフィールド
};
ioBitの構造体は8bitの領域をすべて1bitで分けていることになります。H8のようなマイクロコントローラの入出力は1つのアドレス8bitで、個々のbit単位で入出力が出来ます。これをC言語から使用可能にする方法がビットフィールドです。ここでは、使用しても意味ありませんが、ビット フィールドは、通常の整数と同じように、加減乗除やビット演算に使用できます。ただし、& 演算子でアドレスを取得したり、sizeof 演算子でサイズを取得することはできません。ちなみに、変数領域の下のbitから名前が割り当てられるか、上のbitからかはコンパイラへの指令で変更できます。 |
| アクセス制限 |
|---|
|
static unsigned m_Port; という文があります。これは大域変数(グローバル変数)ですが、staticが先頭に付くとこのソースファイルでのみの大域変数で、他のソースファイルからは参照できないようにしています。 const static unsigned short RESET = 0x0000; は同様ですが、さらに値を変更されないように定数にしています これらはオブジェクト指向言語(C++, java, C#)を意識した作り方になっています。コンストラクタというものはC言語には存在しませんが、コメントに入っていたりします。 |
| volatile型 |
|---|
次のプログラムを見てください。このプログラムはportという変数をチェックしてbit1が立っていれば処理1を行うことを永久に実行する内容です。
int port;
while (1) {
if ((port&2) != 0) {
処理1 // portに対する代入はないものとする
}
}
ところが、賢いコンパイラは(最適化レベルを高めると。普通これがデフォールトだったりする)、portの代入による変更がないので、効率が良くなるように、次のように変更してコンパイルします。普通の変数だったら結果の分かっている計算を何回もするという無駄な時間が費やされます。
int port;
if ((port&2) != 0) {
while (1) {
処理1
}
}
従って、portのチェックは一回しか行わず、IOのポートの場合ではおかしなことになります。volatile型はこのような最適化をさせない型で、組み込み用のプログラムには必須の型です。 |
| CompassHM55B.c |
|---|
#define SHIFT_MSB -1
#define POST_CLOCK_MSB 1
#include "common.h"
void delay(unsigned wait);
int pulseIn(unsigned timeout, unsigned port, int bit, bool pinState);
unsigned char readPin(unsigned int port, int bit);
void setInput(unsigned int port, int bit);
void writePin(unsigned int port, int bit, bool value);
void writePort(unsigned int port, unsigned char value);
void shiftOut(unsigned dataPort, int dPin, unsigned clockPort, int cPin, int bitCount, unsigned short data);
int shiftIn(unsigned dataPort, int dPin, unsigned clockPort, int cPin, int bitCount);
void pulseOut(unsigned length, unsigned port, int bit);
void setOutput(unsigned int port, int bit);
int readPort(unsigned int port);
void CompassReset();
int interpolation(const float x);
struct ioBit{ // Bit Access
unsigned char B7:1; // Bit 7
unsigned char B6:1; // Bit 6
unsigned char B5:1; // Bit 5
unsigned char B4:1; // Bit 4
unsigned char B3:1; // Bit 3
unsigned char B2:1; // Bit 2
unsigned char B1:1; // Bit 1
unsigned char B0:1; // Bit 0
} ;
/**
* この関数の使い方:
*
* // compassのピンの定義
* const int compass_DinDout = 3;
* const int compass_Clk = 0;
* const int compass_En = 4;
*
* // compass のデフォールトの設定をする
* SetDefaultCompassHM55B();
* // compassの詳細な設定をする
* SetCompassHM55B(port, compass_DinDout, compass_Clk, compass_En);
*
* CompassStart()を呼んで計測を開始させる。
* 次のメソッドがある。
* 計測が終了したかどうかを調べるには、CompassPoll() を呼ぶ。
* trueがもどっときたら、getCompassX(), getCompassY とか getCompassAngle()を呼ぶ。
* getCompassAngle()は整数の角度が結果として戻る。
* 次の計測のために再度CompassStart() 呼ぶ。
*
*/
const static unsigned short RESET = 0x0000;
const static unsigned short MEASURE = 0x0008;
const static unsigned short REPORT = 0x000c;
const static unsigned short READY = 0x000c;
static unsigned m_Port;
static int m_DinDout; //pin DinDout
static int m_Clk; //pin CLK
static int m_En; //pin /EN
static int m_x; //x-axis value
static int m_y; //y-axis value
static BYTE PCR=0; // 36064のPCRが馬鹿だから
/**
* コンストラクタ
*
* DinDout: 双方向通信に用いるピン番号
* Clk : シリアルクロック出力に用いるピン番号
* En : チップイネーブルに用いる出力ピン番号
*/
void SetDefaultCompassHM55B() { // デフォールト コンストラクタ
PCR = 0;
m_Port = port2;
m_DinDout = 3;
m_Clk = 0;
m_En = 4;
setOutput(m_Port, m_Clk);
setOutput(m_Port, m_En);
writePin(m_Port, m_Clk, false); //initialize clock pin to low output
writePin(m_Port, m_En, true); //initialize enable pin to high output
CompassReset();
}
void SetCompassHM55B(unsigned port, int DinDout, int Clk, int En) {
PCR = 0; // 全ビット入力になっていることを仮定する
m_Port = port;
m_DinDout = DinDout;
m_Clk = Clk;
m_En = En;
setOutput(port, Clk);
setOutput(port, En);
writePin(port, m_Clk, false); //initialize clock pin to low output
writePin(port, m_En, true); //initialize enable pin to high output
CompassReset();
}
/**
* X方向の値を得る
*
* 戻り: X方向の値
*/
int getCompassX() {
return m_x;
}
/**
* Y方向の値を得る
*
* 戻り: Y方向の値
*/
int getCompassY() {
return m_y;
}
/**
* 方位の角度を得る
*
* 戻り: 角度(0-359).
*/
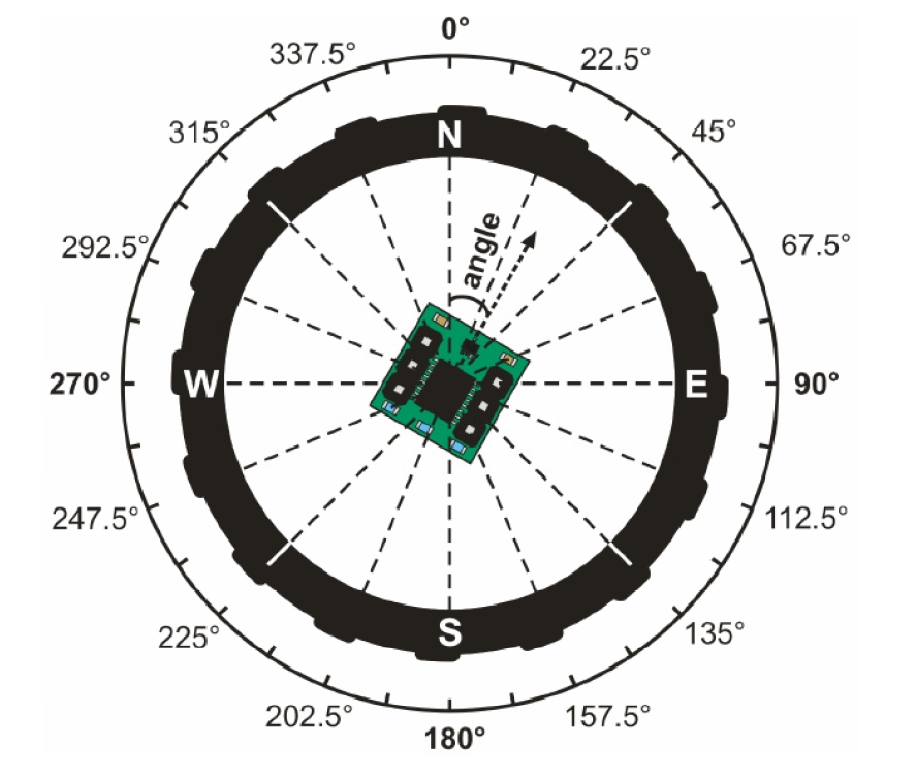
int getCompassAngle() {
return atan2(-m_y, m_x);
// return interpolation((float)atan2(-m_y, m_x));
}
/**
* コンパスをリセットする
*/
void CompassReset() {
writePin(m_Port, m_En, false);
shiftOut(m_Port, m_DinDout, m_Port, m_Clk, 4, RESET);
writePin(m_Port, m_En, true);
}
/**
* コンパスの計測を開始させる
*/
void CompassStart() {
writePin(m_Port, m_En, false);
shiftOut(m_Port, m_DinDout, m_Port, m_Clk, 4, MEASURE);
}
/**
* 計測終了を調べる
*
* 戻り: 計測終了の場合trueそうでない時false
*/
bool CompassPoll() {
bool result;
int m_status;
writePin(m_Port, m_En, true);
writePin(m_Port, m_En, false);
shiftOut(m_Port, m_DinDout, m_Port, m_Clk, 4, REPORT);
m_status = shiftIn(m_Port, m_DinDout, m_Port, m_Clk, 4);
result = (m_status == READY);
if (result) {
m_x = shiftIn(m_Port, m_DinDout, m_Port, m_Clk, 11);
m_y = shiftIn(m_Port, m_DinDout, m_Port, m_Clk, 11);
writePin(m_Port, m_En, true);
if ((m_x & 0x0400) != 0) m_x |= (short)0xF800;
if ((m_y & 0x0400) != 0) m_y |= (short)0xF800;
}
return result;
}
void writePin(unsigned int port, int bit, bool value)
{
switch(bit) {
case 0: (*(volatile struct ioBit *)port).B0 = value; break;
case 1: (*(volatile struct ioBit *)port).B1 = value; break;
case 2: (*(volatile struct ioBit *)port).B2 = value; break;
case 3: (*(volatile struct ioBit *)port).B3 = value; break;
case 4: (*(volatile struct ioBit *)port).B4 = value; break;
case 5: (*(volatile struct ioBit *)port).B5 = value; break;
case 6: (*(volatile struct ioBit *)port).B6 = value; break;
case 7: (*(volatile struct ioBit *)port).B7 = value; break;
}
}
void shiftOut(unsigned dataPort, int dPin, unsigned clockPort, int cPin,
int bitCount, unsigned short data)
{
int i;
int bits;
setOutput(dataPort, dPin); // 直前に入力したかもしれないから
// start()が実行されているとする。
if(bitCount<=0 || 16<bitCount) return;
bits = 1 << (bitCount-1);
for(i=0; i<bitCount; i++, data<<=1) {
if(data & bits) writePin(dataPort, dPin, true);
else writePin(dataPort, dPin, false);
delay(1);
writePin(clockPort, cPin, true); // clock high
delay(1);
writePin(clockPort, cPin, false);
}
delay(1);
}
int shiftIn(unsigned dataPort, int dPin, unsigned clockPort, int cPin, int bitCount)
{
int i;
int data=0;
setOutput(clockPort, cPin);
setInput(dataPort, dPin);
if(bitCount<=0 || 256<bitCount) return 0;
delay(1);
// POST_CLOCK_MSB
writePin(clockPort, cPin, 0);
delay(1);
for(i=0; i<bitCount; i++) {
writePin(clockPort, cPin, 1); // clock high
delay(1);
data<<=1;
if(readPin(dataPort, dPin)) data |= 1;
writePin(clockPort, cPin, 0);
delay(1);
}
return data & 0xffff;
}
// 単位が約5μsのつもり
void delay(unsigned wait)
{
int i;
int n = wait * 2;
for(i=0; i<n; i++);
}
unsigned char readPin(unsigned int port, int bit)
{
unsigned char val = *(volatile unsigned char *)port;
unsigned char Bit = 1 << bit;
return val & Bit;
}
// 他の機能で使われていても、勝手に出力に設定する
void setOutput(unsigned int port, int bit)
{
PCR |= 1 << bit;
*(volatile unsigned char *)(port + 0x10) = PCR;
}
// ほかの機能で使われていても、勝手に入力に設定する
void setInput(unsigned int port, int bit)
{
int Bit = 1<<bit;
PCR &= ~Bit;
*(volatile unsigned char *)(port + 0x10) = PCR;
}
/**
* 線形補間を用いて値を補正する
*
*/
int interpolation(const float x){
float ar[17]={0,36,59,84,100,126,145,158,172,194,211,228,253,280,306,337,360};
int i;
float y=0, z;
for(i=1;i<16;i++){
y = 22.5*i;
if(y>=x) break;
}
if(i==16) y=360;
z = y-22.5;
// y=yi + (yi+1-yi)(x-xi)/(xi+1-xi) を行い値を返す
z = ar[i-1]+(((ar[i]-ar[i-1])*(x-z))/(y-z));
return (int)(z+0.5);
}
|
| IntegerMath.c |
|---|
// filename: IntegerMath.c
typedef unsigned char bool;
#define false 0
#define true 1
static int abs(int x) {
if (x == -32768) x = 0;
return (x < 0) ? -x : x;
}
/* x: (0-359)
* 戻り値 truncated int(100*sin(angle))
* 範囲 -100 to +100
*/
static int sign(int x) {
return (x == 0) ? 0 : (x<0) ? -1 : 1;
}
static int cos(int angle) {
int qop = angle;
int div = 101;
/* perform quadrant conversion */
/* (input is 0 to 359) */
if (angle > 90) {
qop = 180 - angle;
if (angle < 270) div = -101;
}
if (angle > 180) qop = angle - 180;
if (angle > 270) qop = 360 - angle;
/* quadratic fit for quadrant */
return ((10188 - qop * (qop + 23)) / div);
}
static int sin(int angle) {
return cos((angle+270)%360);
}
/**
* arctan(y/x)
*
* y: y-value
* x: x-value (0であってはいけない)
*/
/* オーバーフローを防ぐため引数は1000以下にする */
int atan2(int y, int x) {
int ax;
int ay;
int aq=0;
bool flip = false;
// 第一象限で計算する
ax = abs(x);
ay = abs(y);
// ax >= ay の場合で近似する
if (ax < ay) {
aq = ax;
ax = ay;
ay = aq;
flip = true;
}
// 0の値の対処をする */
if (ay != 0) {
aq = (30 * ax) / ay;
if (aq == 0) {
aq = 90;
}
else {
if (aq >= 82) {
aq = 1720 / aq;
}
else {
aq = 1720 / (aq + 8);
}
}
}
else {
// atan2(0,0) は駄目
//if (ax == 0) //aq = aq / 0;
aq = 0;
}
// ひっくり返したものを元に戻す
if (flip) aq = 90 - aq;
// 正しい象限に戻す
if (x < 0) {
if (y < 0) {
// 第三象限
aq = 180 + aq;
}
else {
// 第二象限
aq = 180 - aq;
}
}
else {
if (y < 0) aq = 360 - aq;
}
// 0~359の間にする
return (aq % 360);
}
|
| もう少し考えてみよう。プログラムがスマートになる。 |
|---|
|
CompassHM55B.cのグローバル変数にPCRという変数があります。 static BYTE PCR=0; // 36064のPCRが馬鹿だから 「36064のPCRが馬鹿だから」というコメントの意味は、PCRが書き込みのみで、読み込みが出来ないのと、ビットアクセスができない二重苦だからです。CompassHM55B.cではこの変数を読むことで入出力の状態を知り新しくそのビットの入出力方向を変更することができるようにしています。何故こんな面倒な事をしているかといえば、PCRがバイトアクセスしかできない設定になっているからです。従って、簡単にコントロールするにはビットアクセスできるようにiodefine.hの設定を変えてしまえば良いということが分かります。 これはシステムの設定の変更なのでちょっと勇気が要ります。ここでは、PCR1からPCR7までを変更してみます。これに伴って、vs-wrc003.cの修正が必要になります。これは各自行ってください。
CompassHM55B.cに関しては、PCRに関する行を全て削除します。
また、setOutputとsetInputの関数を以下のように変更します。
// 他の機能で使われていても、勝手に出力に設定する
void setOutput(unsigned int port, int bit)
{
port += 0x10;
writePin(port, bit, 1);
}
// ほかの機能で使われていても、勝手に入力に設定する
void setInput(unsigned int port, int bit)
{
port += 0x10;
writePin(port, bit, 0);
}
|
| iodefine.hの一部を変更する |
|---|
union { /* PCR1 */
unsigned char BYTE; /* Byte Access */
struct { /* Bit Access */
unsigned char B7:1; /* Bit 7 */
unsigned char B6:1; /* Bit 6 */
unsigned char B5:1; /* Bit 5 */
unsigned char B4:1; /* Bit 4 */
unsigned char :1; /* Bit 3 */
unsigned char B2:1; /* Bit 2 */
unsigned char B1:1; /* Bit 1 */
unsigned char B0:1; /* Bit 0 */
} BIT; /* */
} PCR1; /* */
union { /* PCR2 */
unsigned char BYTE; /* Byte Access */
struct { /* Bit Access */
unsigned char :1; /* Bit 7 */
unsigned char :1; /* Bit 6 */
unsigned char :1; /* Bit 5 */
unsigned char B4:1; /* Bit 4 */
unsigned char B3:1; /* Bit 3 */
unsigned char B2:1; /* Bit 2 */
unsigned char B1:1; /* Bit 1 */
unsigned char B0:1; /* Bit 0 */
} BIT; /* */
} PCR2; /* */
union { /* PCR3 */
unsigned char BYTE; /* Byte Access */
struct { /* Bit Access */
unsigned char B7:1; /* Bit 7 */
unsigned char B6:1; /* Bit 6 */
unsigned char B5:1; /* Bit 5 */
unsigned char B4:1; /* Bit 4 */
unsigned char B3:1; /* Bit 3 */
unsigned char B2:1; /* Bit 2 */
unsigned char B1:1; /* Bit 1 */
unsigned char B0:1; /* Bit 0 */
} BIT; /* */
} PCR3; /* */
char wk6; /* */
union { /* PCR5 */
unsigned char BYTE; /* Byte Access */
struct { /* Bit Access */
unsigned char B7:1; /* Bit 7 */
unsigned char B6:1; /* Bit 6 */
unsigned char B5:1; /* Bit 5 */
unsigned char B4:1; /* Bit 4 */
unsigned char B3:1; /* Bit 3 */
unsigned char B2:1; /* Bit 2 */
unsigned char B1:1; /* Bit 1 */
unsigned char B0:1; /* Bit 0 */
} BIT; /* */
} PCR5; /* */
union { /* PCR6 */
unsigned char BYTE; /* Byte Access */
struct { /* Bit Access */
unsigned char B7:1; /* Bit 7 */
unsigned char B6:1; /* Bit 6 */
unsigned char B5:1; /* Bit 5 */
unsigned char B4:1; /* Bit 4 */
unsigned char B3:1; /* Bit 3 */
unsigned char B2:1; /* Bit 2 */
unsigned char B1:1; /* Bit 1 */
unsigned char B0:1; /* Bit 0 */
} BIT; /* */
} PCR6; /* */
union { /* PCR7 */
unsigned char BYTE; /* Byte Access */
struct { /* Bit Access */
unsigned char :1; /* Bit 7 */
unsigned char B6:1; /* Bit 6 */
unsigned char B5:1; /* Bit 5 */
unsigned char B4:1; /* Bit 4 */
unsigned char :1; /* Bit 3 */
unsigned char B2:1; /* Bit 2 */
unsigned char B1:1; /* Bit 1 */
unsigned char B0:1; /* Bit 0 */
} BIT; /* */
} PCR7; /* */
union { /* PCR8 */
unsigned char BYTE; /* Byte Access */
struct { /* Bit Access */
unsigned char B7:1; /* Bit 7 */
unsigned char B6:1; /* Bit 6 */
unsigned char B5:1; /* Bit 5 */
unsigned char :1; /* Bit 4 */
unsigned char :1; /* Bit 3 */
unsigned char :1; /* Bit 2 */
unsigned char :1; /* Bit 1 */
unsigned char :1; /* Bit 0 */
} BIT; /* */
} PCR8; /* */
|